

Atypical Aflutter may have varying AV conduction, which can cause an irregular heart rhythm.
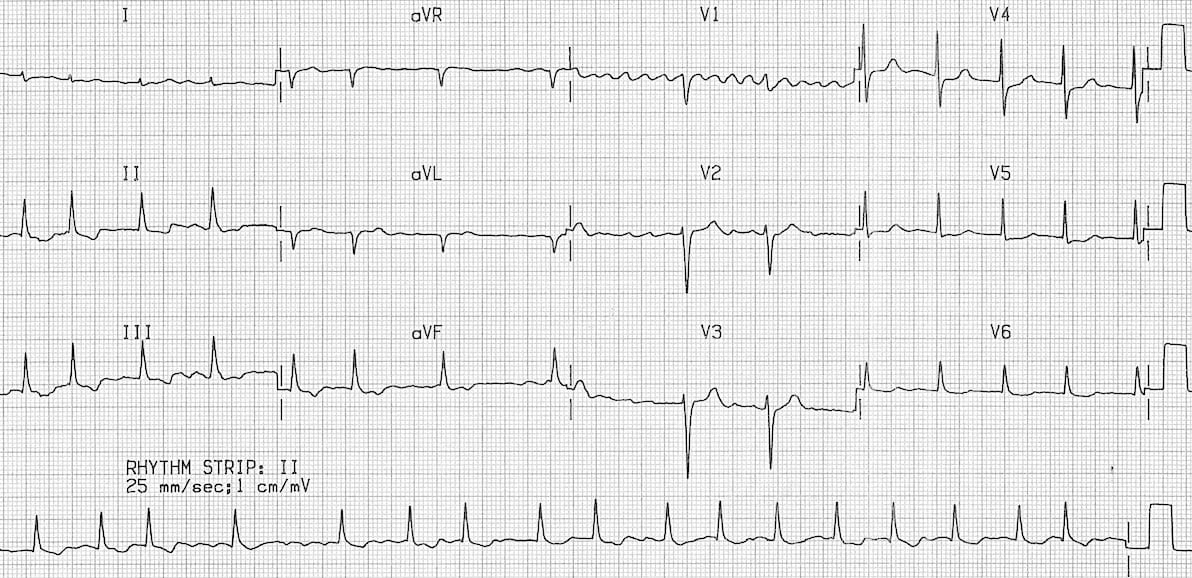
‘Coarse Afib’ has an “f” wave amplitude> 0.5 mm, which can mimic Aflutter “f” waves morphology. It may be difficult to distinguish atypical Aflutter from coarse Afib. In patients subjected to cardiac surgery or catheter ablation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation or showing atypical ECG patterns, macro-re-entrant and focal tachycardia mechanisms can be very complex and electrophysiological studies are necessary to guide ablation treatment in poorly tolerated cases. Heart rate ” Irregularly irregular” and variable (slow Afib 100 bpm)įig.2 Atrial fibrillation ECG (with Ashmann phenomenon)ĭistinguish atypical Aflutter from coarse Afib:.The narrow complex rhythm is therefore a junctional escape. Atypical (type II) atrial flutter: doesn’t fulfill the criteria for typical atrial flutter Coarse atrial fibrillation (irregular baseline with atrial complexes at rate > 400 bpm) The combination of atrial fibrillation with a regular rhythm (regularised AF) indicates that none of the atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles, i.e.Clockwise: positive flutter waves in II, III, aVF and negative in V1.Counterclockwise: negative flutter waves in II, III, aVF and positive in V1.11 It often begins as short periods of abnormal beating, which become longer or continuous over time. Typical (type I) atrial flutter: saw-tooth-like waves Although the symptoms of atrial flutter can be similar to atrial fibrillation, your doctor should be able to identify the different arrhythmias through an ecg. 193,300 with atrial flutter (2015) 10 Atrial fibrillation ( AF or A-fib) is an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by rapid and irregular beating of the atrial chambers of the heart.(Usually, the heart beats 60 to 150 times a minute. 300 bpm (200-400 bpm) with a heart rate typically ca. Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is an unusually fast heartbeat in the heart’s upper chambers, sometimes as many as 400 beats or more a minute. Afib and atypical Aflutter requires more expertise and radiofrequency ablation has lower success rate.Ītrial rate ca. Atrial fibrillation is another type of atrial tachycardia that is closely related to atrial flutter. The difference between atrial fibrillation (Afib) and atrial flutter (Aflutter), is clinically relevant because typical flutter can easily be treated by radiofrequency ablation. Atrial flutter is a type of atrial tachycardia that results in an arrhythmia (rhythm disorder or not a normal rhythm) where the atria of the heartbeat too quickly in a fast, usually regular, rhythm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
